Are Styes Caused By Stress
Have you ever wondered if stress can actually cause styes? It’s a common question, and it’s understandable why people might think there could be a relationship between the two. After all, stress can wreak havoc on our bodies and cause all kinds of health issues. So, could styes be one of them? Let’s dive into this topic and find out!
When it comes to styes, the truth is that stress alone is not the direct cause of these annoying eye infections. Styes are typically caused by a bacteria called staphylococcus aureus, which is commonly found on our skin. However, stress can indirectly contribute to the development of styes. When we’re stressed, our immune system can become compromised, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. Additionally, stress can lead to poor habits, such as rubbing or touching our eyes more frequently, which can introduce bacteria into the area and increase the risk of stye formation. In this article, we’ll explore the relationship between stress and styes in more detail and provide some tips on how to prevent and manage them. So, if you’re curious to learn more, keep reading!
Are Styes Caused By Stress
What is a Stye?
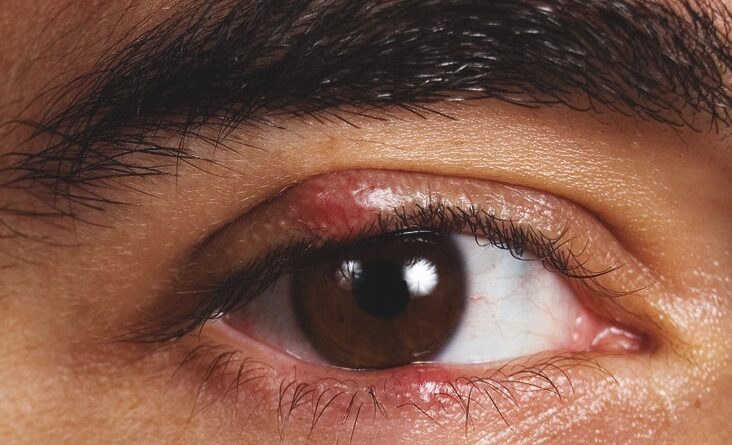
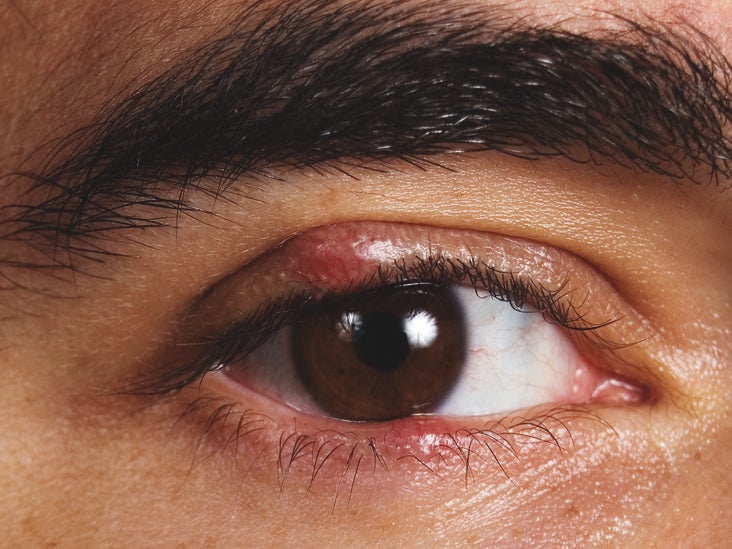
A stye, also known as a hordeolum, is a common eye condition that many people experience at some point in their lives. It is a small, painful bump that typically appears on the eyelid or the base of the eyelashes. Styes can be unsightly and uncomfortable, causing redness, swelling, and irritation. While they are usually harmless and resolve on their own within a week or two, understanding the causes and potential risk factors can help prevent their occurrence.
Definition of a Stye
A stye is a localized infection or inflammation of the eyelid or the glands that produce oil to lubricate the eyes. It can occur on the inside or outside of the eyelid and is often caused by the blocking of oil glands or the presence of bacteria. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common bacteria associated with stye formation.
Symptoms of a Stye
The most noticeable symptom of a stye is the appearance of a red, swollen bump on the eyelid. This bump is usually filled with pus and may be tender to the touch. Other common symptoms include pain, itchiness, sensitivity to light, and excessive tearing. In some cases, styes can also cause blurred vision or a feeling of grittiness in the eye.
Causes of a Stye
Styes are typically caused by a combination of factors, including bacterial infection, poor hygiene practices, and compromised immune system. Bacterial infection occurs when the bacteria present on the skin or in the eye find their way into the oil glands of the eyelids, leading to inflammation and the formation of a stye. Poor hygiene practices, such as touching the eyes with dirty hands or using expired eye makeup, can also contribute to the development of styes. Additionally, individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to infections, including styes.
Understanding Stress
Stress is a natural response to demanding or threatening situations. It is the body’s way of preparing for a fight-or-flight response and can manifest in various physical, emotional, and cognitive symptoms. While stress is a normal part of life, excessive or chronic stress can have detrimental effects on overall health and well-being.
Definition of Stress
Stress can be defined as the body’s response to external pressures or internal demands that exceed an individual’s ability to cope. It can be triggered by various factors, including work-related deadlines, relationship problems, financial difficulties, or traumatic events. When stress becomes overwhelming or prolonged, it can negatively impact physical and mental health.
Types of Stress
There are different types of stress that individuals may experience. Acute stress is short-term stress that occurs in response to a specific event or situation. It is often referred to as “fight-or-flight” stress and is characterized by an immediate physiological response, such as an increased heart rate or heightened alertness. Chronic stress, on the other hand, is long-term stress that persists over an extended period. It can result from ongoing issues like job dissatisfaction, chronic illness, or relationship conflicts.
Effects of Stress on the Body
Stress can impact the body in various ways, including physiological, emotional, and behavioral changes. Physiologically, stress triggers the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which prepare the body for action by increasing heart rate, elevating blood pressure, and boosting energy levels. Over time, chronic stress can lead to negative health outcomes, such as cardiovascular problems, weakened immune system, digestive issues, and mental health disorders like anxiety and depression.

Connection Between Stress and Styes
Research has suggested a potential link between stress and the formation of styes. While stress alone may not directly cause styes, it can weaken the immune system and increase susceptibility to infections, including those that contribute to stye formation.
Research on Stress and Styes
Multiple studies have explored the relationship between stress and stye occurrence. A study published in the Journal of Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science found that individuals with elevated stress levels were more likely to develop styes compared to those with lower stress levels. Another study conducted by researchers at the University of California, San Francisco, found that stress can prolong the healing time of styes and increase the risk of recurrence.
Potential Link Between Stress and Stye Formation
While the exact mechanism behind the link between stress and styes is still not fully understood, it is believed that stress may disrupt the balance of the immune system, making it less effective in defending against bacterial infections. Stress hormones, such as cortisol, have been shown to suppress immune system functions, impairing the body’s ability to fight off infections. Consequently, this weakened immune response may increase the likelihood of developing styes.
Effects of Stress on the Immune System
Chronic stress can have profound effects on the immune system, compromising its ability to protect the body from infections and illnesses. Prolonged stress can lead to an overactive immune response, referred to as chronic low-grade inflammation, which can cause a range of health problems, including increased susceptibility to infections. This dysregulation of the immune system can contribute to the development and persistence of styes.
Other Causes of Styes
While stress may play a role in the formation of styes, it is important to note that there are other causes as well. Understanding these factors can help individuals take appropriate measures to prevent stye occurrence.
Bacterial Infection
The most common cause of styes is a bacterial infection, often caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. When these bacteria enter the oil glands of the eyelids, they can cause inflammation and the formation of a stye. Bacterial infections can occur when individuals touch their eyes with unwashed hands or use contaminated eye makeup or contact lenses.
Poor Hygiene Practices
Improper hygiene practices can also contribute to the development of styes. Touching the eyes with dirty hands, failing to wash off eye makeup before sleeping, or using expired cosmetics can introduce bacteria into the eyelids and increase the risk of stye formation. It is important to maintain good hygiene habits, including regular handwashing and proper cleaning of contact lenses and eye makeup.
Compromised Immune System
Individuals with compromised immune systems are more susceptible to infections, including styes. Factors that can weaken the immune system include chronic illnesses, certain medications, nutritional deficiencies, and high levels of stress. It is crucial for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or immunocompromised statuses to take extra precautions to minimize the risk of styes.
Managing Stress to Prevent Styes
To prevent styes and promote overall eye health, it is important to effectively manage stress levels. Implementing stress management techniques and adopting self-care practices can help reduce the occurrence and severity of styes.
Stress Management Techniques
Several stress management techniques can be beneficial in preventing stye formation. These include practicing relaxation exercises like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, can also help reduce stress levels. Additionally, finding healthy ways to cope with stress, such as talking to a supportive friend or family member, journaling, or engaging in hobbies, can be helpful in managing stress.
Self-Care Practices
Taking care of oneself is essential for maintaining overall well-being and preventing styes. Getting adequate sleep, eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, and staying hydrated can support a healthy immune system and minimize the risk of infections. It is also important to avoid excessive rubbing or touching of the eyes, as this can introduce bacteria and irritants, leading to styes.
Seeking Professional Help
If stress is becoming overwhelming or significantly impacting daily life, it may be beneficial to seek professional help. Mental health professionals, such as psychologists or therapists, can provide guidance and support in managing stress effectively. They can help develop personalized coping strategies and provide tools to navigate stressful situations.
Tips for Stye Prevention
In addition to managing stress, there are several steps individuals can take to prevent styes and maintain optimal eye health.
Maintaining Good Hygiene
Practicing good hygiene habits is crucial in preventing stye formation. This includes regular handwashing with soap and water, especially before touching the eyes or applying eye drops. It is important to avoid sharing eye makeup or contact lenses and regularly clean cosmetic brushes and applicators.
Avoiding Rubbing or Touching the Eyes
Rubbing or touching the eyes with dirty hands can introduce bacteria and irritants, increasing the likelihood of stye formation. It is important to resist the urge to rub the eyes and to use a clean tissue or cotton swab to gently remove any debris or irritation.
Using Clean Cosmetics and Contact Lenses
Using clean and properly stored cosmetics, such as mascara, eyeliner, or eye shadows, can prevent bacterial contamination and reduce the risk of styes. Additionally, proper care and cleaning of contact lenses, as per the manufacturer’s instructions, can minimize the chances of eye infections and stye formation.

Treatment Options for Styes
While most styes will resolve on their own within a week or two, there are various treatment options available to alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
Home Remedies for Stye Relief
Home remedies can provide relief and expedite the healing process for styes. Applying warm compresses to the affected area for 10 to 15 minutes, several times a day, can help reduce inflammation and facilitate drainage of the stye. It is important to avoid squeezing or popping the stye, as this can worsen the infection.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate pain and discomfort associated with styes. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking any medications, especially if there are underlying health conditions or if currently taking other medications.
Medical Procedures for Severe Cases
In severe or persistent cases of styes, medical intervention may be required. An eye specialist, such as an ophthalmologist, may drain the stye by making a small incision or prescribe antibiotic eye drops or ointments to treat the infection. These procedures should only be performed by a trained healthcare professional and under proper medical supervision.
When to See a Doctor
While most styes do not require immediate medical attention, there are certain signs that indicate the need for prompt treatment.
Signs that Require Medical Attention
It is important to seek medical attention if the stye worsens or does not improve within a week or two. Signs that require immediate attention include severe pain, excessive swelling or redness, vision changes, or the development of fever and chills. These symptoms may indicate a more serious infection or the need for medical intervention.
Consulting with an Eye Specialist
If styes are recurrent or frequently occurring, it may be helpful to consult with an eye specialist. An ophthalmologist can assess the underlying causes and provide appropriate treatment options to prevent future styes. They can also address any concerns or questions regarding eye health.
Seeking Prompt Treatment
While styes are usually harmless and resolve on their own, prompt treatment is important to prevent complications or further infection. It is advisable to seek medical advice if there are any doubts or concerns regarding the stye or if symptoms worsen despite home remedies or over-the-counter treatments.

Prevalence of Styes
Styes are a common eye condition that affects people of all ages. While exact statistics on stye occurrence may vary, they are widespread and can occur in both children and adults.
Statistics on Stye Occurrence
According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, approximately 200,000 cases of styes are reported in the United States each year. Styes can affect individuals of all ages, but they are more common in adults over the age of 40. They can occur in both men and women, with no significant gender differences.
Common Demographics Affected by Styes
Styes can affect individuals from all walks of life, regardless of age, gender, or race. However, certain factors may increase the likelihood of stye occurrence. Individuals with compromised immune systems, those prone to allergies, or those with pre-existing eye conditions may be at higher risk for developing styes.
Risk Factors for Developing Styes
Several risk factors can increase an individual’s susceptibility to stye formation. These include:
- Chronic or recurrent styes
- Pre-existing dry eye syndrome
- Diabetes or other chronic illnesses
- Immunodeficiency disorders
- Use of contact lenses
- Poor hygiene practices
- Pre-existing eye infections
Conclusion
While stress alone may not directly cause stye formation, research suggests a potential link between stress and styes, with stress potentially weakening the immune system and increasing susceptibility to infections. However, it is important to remember that styes can have multiple causes, including bacterial infection, poor hygiene practices, and compromised immune systems. To prevent styes, it is essential to manage stress effectively, practice good hygiene, and seek professional help if stress becomes overwhelming. By adopting these strategies and maintaining good eye health practices, individuals can reduce the risk of stye formation and promote overall well-being.